Plots
mPAP
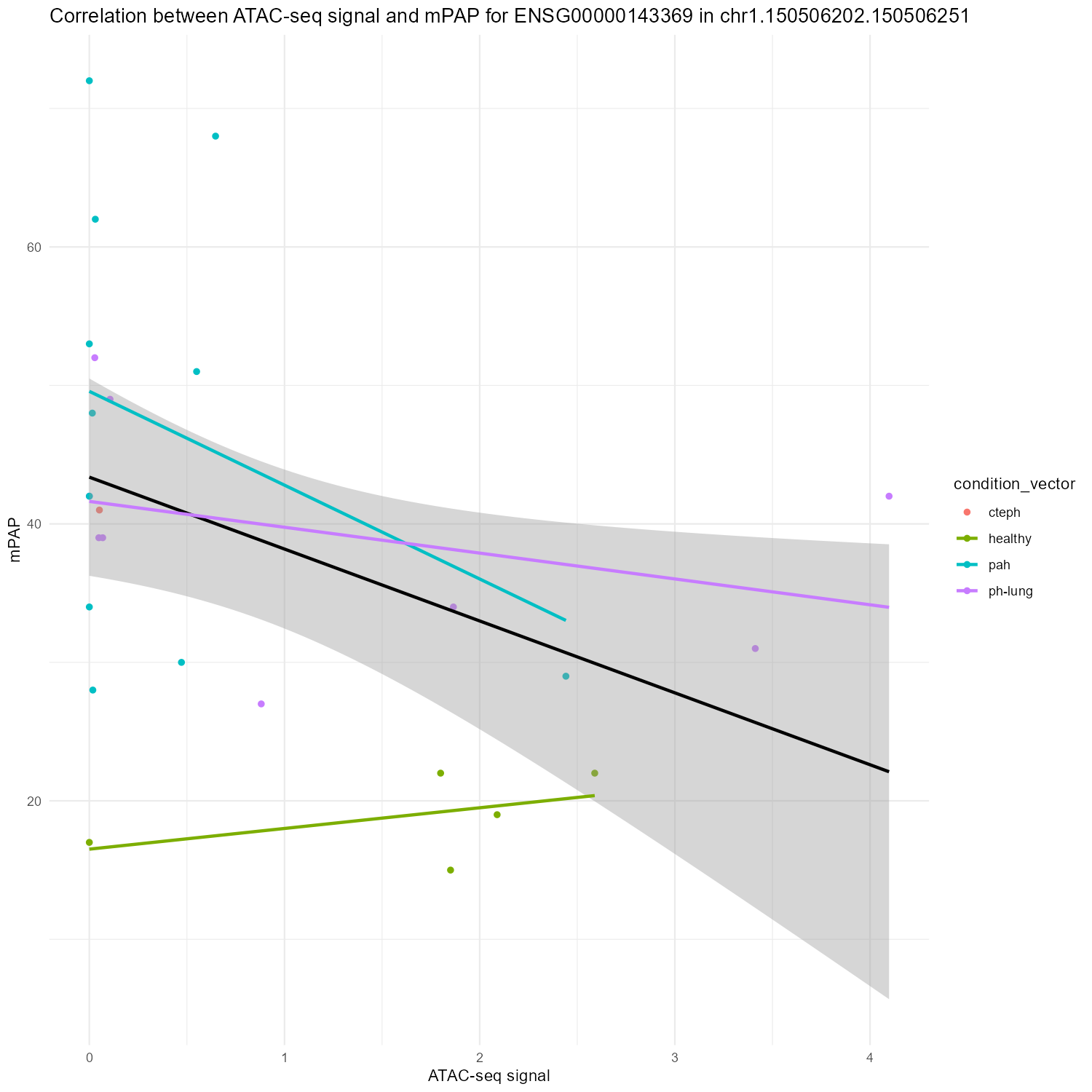
Info
Hardy, Sean A., et al. "Extracellular Matrix Protein-1 as a Mediator of Inflammation-Induced Fibrosis After Myocardial Infarction." Basic to Translational Science 8.12 (2023): 1539-1554.
NCBI Gene Summary for ECM1 Gene
- This gene encodes a soluble protein that is involved in endochondral bone formation, angiogenesis, and tumor biology. It also interacts with a variety of extracellular and structural proteins, contributing to the maintenance of skin integrity and homeostasis. Mutations in this gene are associated with lipoid proteinosis disorder (also known as hyalinosis cutis et mucosae or Urbach-Wiethe disease) that is characterized by generalized thickening of skin, mucosae and certain viscera. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]
GeneCards Summary for ECM1 Gene
ECM1 (Extracellular Matrix Protein 1) is a Protein Coding gene. Diseases associated with ECM1 include Lipoid Proteinosis Of Urbach And Wiethe and Inflammatory Bowel Disease 1. Among its related pathways are Integrin Pathway and ERK Signaling. Gene Ontology (GO) annotations related to this gene include enzyme binding and obsolete protein C-terminus binding.
Interactive Graph